Biodiversity Risk Assessment & Water Risk Management Programs
Biodiversity and Natural Capital Risk Identification and Management
The food industry is one of the sectors with high dependency on and impact to natural capital. Pulmuone recognizes the importance of natural capital and is making various efforts for natural capital conservation and biodiversity risk management.
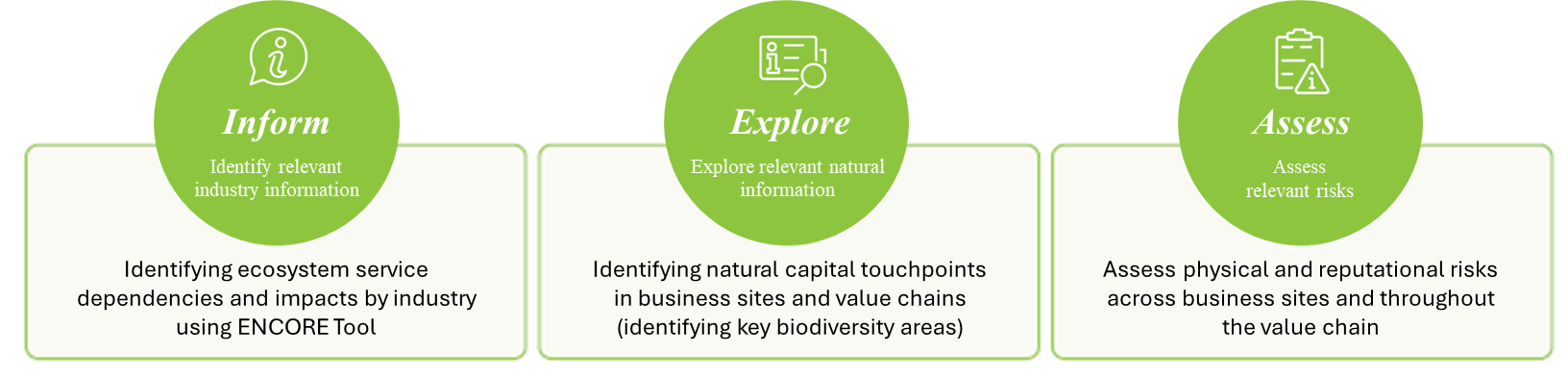
To this end, Pulmuone aims to systematically assess dependencies and impacts related to biodiversity and natural capital and manage associated risks and opportunities by utilizing the LEAP methodology presented by TNFD (Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures), along with ENCORE and WWF Risk Filter Tool. Additionally, through Session D, the supreme decision-making body for environmental and social responsibility management, the company carries out roles and responsibilities for biodiversity activities, management strategies, and risk response.
These efforts are integrated into the company-wide ESG risk management framework, and Pulmuone plans to continuously enhance its natural capital and biodiversity risk assessment and response activities going forward.
Biodiversity and Natural Capital Risk Assessment Process
Location-based Biodiversity Dependency and Impact Assessment
Pulmuone evaluates dependencies and impacts on 'Protected Areas' and 'Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA)' at business sites and surrounding regions using environmental factors, one of the WWF Biodiversity risk assessment criteria. According to the sensitive area criteria defined by TNFD, the 2023 assessment results identified a total of 21 business sites with high and very high dependencies and impacts on protected areas and key biodiversity areas.
To identify impacts on conservation and protected areas, the assessment was conducted using the World Database of Protected Areas (WDPA) from the UNEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre (WCMC). This process analyzed terrestrial and marine unit-based risks based on IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) protected area categories I-IV and unclassified protected areas. IUCN protected area categories are classified from I (strict nature reserves) to IV (habitat and species management areas) according to the degree of nature conservation, with areas having higher protection intensity having greater conservation value and stricter restrictions on development activities. In the ‘Results of Risk and Impact Assessments’ table, business sites with more than 30% overlap with protected areas in categories I–IV were classified as ‘very high risk’ and included in the aggregated results accordingly.
Activity-based Biodiversity Dependency and Impact Assessment
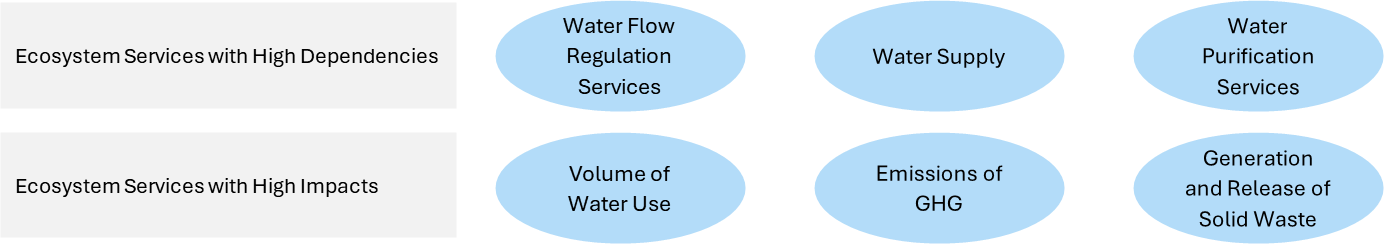
Pulmuone uses ENCORE (Exploring Natural Capital Opportunities, Risks, and Exposure), an online tool recommended by TNFD, to assess dependencies and impacts on ecosystem services based on business activities across the entire value chain. The value chain is classified into 19 activities based on ISIC (International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities), and ENCORE assessment results are converted to a 5-point scale from Very Low to Very High, listing ecosystem services in order from highest to lowest dependency and impact. The assessment results showed that, in terms of dependencies, the company is highly dependent on ecosystem services such as water flow regulation, water supply, and water purification, in that order. This indicates a significant reliance on the stable availability of clean water resources. In terms of impacts, it was confirmed that the company exerts pressure on nature primarily through water consumption, followed by greenhouse gas emissions and solid waste discharge.
Ecosystem Services with High Dependencies and Impacts from Pulmuone's Business Activities
Biodiversity Risk Assessment
In 2024, Pulmuone conducted a biodiversity and natural capital risk assessment covering 115 business sites and regions in six countries using the WWF Biodiversity Risk Filter tool. Based on the Locate, Evaluate, Assess, and Prepare (LEAP) framework developed by the TNFD, this tool supports a location-specific risk analysis approach, using latitude, longitude, region, and watershed-level data to assess site-specific vulnerabilities and impacts.
Physical risk is evaluated across five categories: (1) Provisioning Services; (2) Regulating & Supporting Services – Enabling; (3) Regulating Services – Mitigating; (4) Cultural Services; and (5) Biodiversity Pressure. Reputational risk is evaluated based on three factors: (6) Environmental Factors; (7) Socioeconomic Factors; and (8) Additional Reputational Factors. Final risk scores are determined by aggregating both physical and reputational risks on a five-point scale, with higher scores indicating greater risk severity.
According to the 2023 assessment, regions with high-risk levels (scoring 3.4 and above) were primarily concentrated in Korea. Out of the 115 locations assessed, 67 sites (58%) were classified as high-risk (high and very high ratings). Among these, 16 sites were evaluated as having both high physical and reputational risks. Two business sites were identified as having very high physical risk: a soybean supplier in Cheongju and a packaging material supplier in the Gyeonggi region. No sites were found to have very high reputational risk.
※ Biodiversity assessment results can be found on p.66 of the Integrated Report.
Risk Assessment of Company Business Sites for Priority Ecosystem Services
Pulmuone conducted risk assessments based on ecosystem service types for water resources, solid waste, and climate change, which represent the company's most significant areas of dependency and impact. For water resources, the WWF Water Risk Filter was used to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of physical risks (e.g. water scarcity, water quality degradation, and water source stability), regulatory risks (e.g. wastewater quality and compliance with water-related regulations), and reputational risks (e.g. stakeholder perception and exposure to water-related concerns). This tool was also applied to assess ecosystem vulnerability within the watersheds where Pulmuone's business sites are located.
Among the key water-related ecosystem services—flow regulation, water supply, and water purification—risk assessment results showed average scores of 3.1 for domestic sites and 3.2 for overseas sites, both indicating a moderate level of risk. However, four risk categories at domestic sites and six at overseas sites recorded high risk levels of 4.0 points or higher. Domestic sites exhibited the highest risk in coastal eutrophication potential (5.0) and wetland degradation (4.9), while overseas sites showed elevated risk in wetland degradation (4.7), biochemical oxygen demand (4.3), coastal eutrophication potential (4.2), and pesticide contamination risk (4.2).
For ecosystem services beyond water resources, namely greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and solid waste discharge, risks were assessed using the WWF Biodiversity Risk Filter Tool. Evaluation of risk items related to GHG emissions, such as extreme heat and tropical cyclones, and to solid waste, such as pollution-related risks, revealed that domestic business sites face elevated risk from tropical cyclones (e.g., typhoons), while overseas sites are more exposed to pollution-related risks, with scores of 4.0 and 3.7, respectively.
Number of Manufacturing Facilities in Water-Stressed Areas

Supply Chain Risk Assessment for Priority Ecosystem Services
Following the company-level assessment, Pulmuone conducted risk evaluations for water resources, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and solid waste across its supply chain.
For water-related ecosystem services—flow regulation, water supply, and water purification—both upstream (e.g., raw material sources and partner companies) and downstream (e.g., logistics centers and retail services) segments recorded an average risk score of 3.2, indicating a moderate level of risk. However, seven categories showed high risk levels of 4.0 points or above across both upstream and downstream segments. In the upstream segment, the highest risk levels were observed in coastal eutrophication potential (raw material sources: 4.2; partner companies: 5.0) and wetland degradation (raw material sources: 4.7; partner companies: 5.0). In the downstream segment, distribution centers and retail stores showed elevated risks in coastal eutrophication potential (4.6 and 4.8, respectively), as well as in total dissolved solids discharge and wetland degradation (4.6 and 4.7, respectively).
Consistent with the assessment of company-operated sites, supply chain risks associated with GHG emissions and solid waste discharge were evaluated using detailed results from the WWF Biodiversity Risk Filter Tool. Notably, raw material sources showed high risk scores for extreme heat (4.0), tropical cyclones (4.2), and pollution (4.3). Upstream partner companies and downstream logistics and retail facilities also exhibited elevated risks, particularly for tropical cyclones and pollution, with scores of 4.0 or higher.
To further examine raw material supply risks, water-related risks in raw material origin regions were analyzed in greater detail. The results identified high water stress regions including Ontario (Canada); Inner Mongolia, Liaoning Province, and Shandong (China); and the western United States. In addition, domestic raw material supply chains also exhibited elevated baseline water stress levels.
Proportion of Agricultural Products Produced in Water-Stressed Areas

Pulmuone's Biodiversity Risks and Response Strategies
Pulmuone identifies risks based on assessment results and establishes corresponding response strategies. Biodiversity risks, alongside climate change risks, are categorized and managed according to their nature. Physical risks are classified as operational risks, while transition and market risks are managed as operational, compliance, or strategic risks depending on their characteristics.
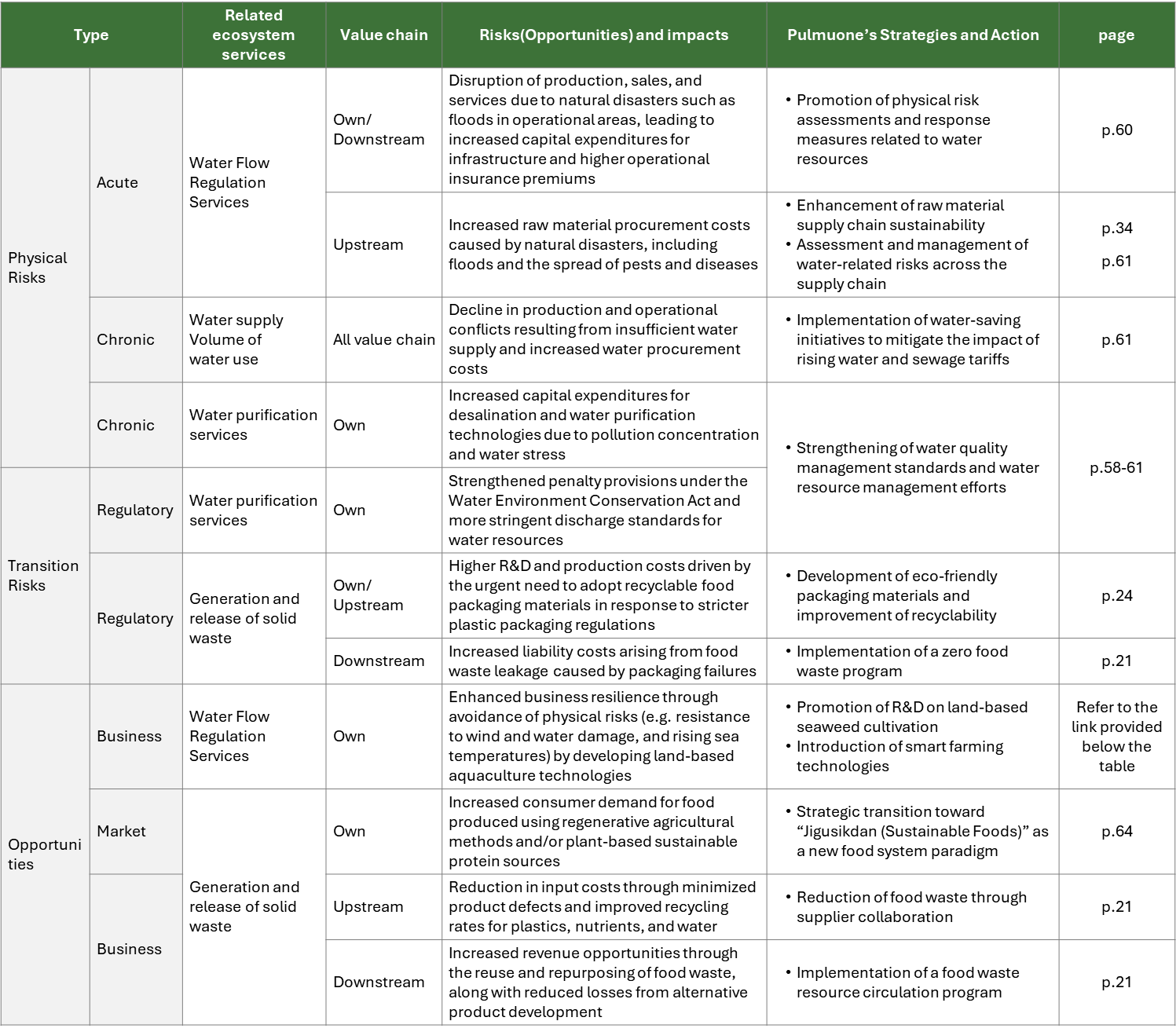
※ Pulmuone's Climate Change Risks and Response Strategies :
https://sustainability.pulmuone.co.kr/en/main/contentsView.do?id_su_bbs=273&id_su_category=
※ Promotion of R&D on land-based seaweed cultivation :
https://www.khan.co.kr/article/202407092120005